Addiction affects millions of people and their families. “What’s the cycle of addiction?” is a common question from people who are learning about addiction treatment and looking for a way to turn their lives around. The cycle of addiction involves different stages, leading to dependence, relapse, and struggles with recovery. Learning what drives this cycle helps address the needs of those affected and provides strategies to break free.
What Drives the Cycle of Addiction?
Biological, psychological, and environmental factors fuel the addiction cycle. Many people experiment with drugs or alcohol due to curiosity, peer pressure, or stress relief. This first use changes brain chemistry, reinforcing the behavior and leading to repeated substance use. Over time, dependency develops, making it harder to stop without professional help.
Genetics, trauma, and mental health issues also influence addiction. A family history of substance use disorder increases the likelihood of addiction. Trauma, especially during childhood, often leads people to use drugs or alcohol as a coping mechanism. These factors create a destructive cycle that makes quitting more difficult. Breaking this cycle requires a comprehensive plan that addresses these underlying issues and provides the necessary support.
Stages of Addiction Explained
The stages of addiction explained to someone who is struggling with addiction can sound familiar when they look back on their lives. They start with experimentation, leading to more serious substance abuse. Occasional use begins without recognition of the risks. As use continues, reliance on drugs or alcohol increases. Tolerance develops, requiring higher doses for the same effect. This pattern leads to dependence, where the body adapts to the substance, resulting in withdrawal symptoms when stopping.
As addiction deepens, personal and professional lives suffer. Relationships deteriorate, and responsibilities go ignored. The focus shifts entirely to obtaining and using the substance. Feelings of guilt or shame often push people further into addiction. Without intervention, substance use disorder takes hold, making recovery more difficult.
The Stages That Keep Addiction Going
The addiction cycle includes distinct stages that reinforce each other. The first stage involves initial substance use, often influenced by curiosity or social pressure. Continued use leads to cravings and tolerance, driving compulsive behavior. In the next stage, addiction causes health problems, broken relationships, and legal troubles.
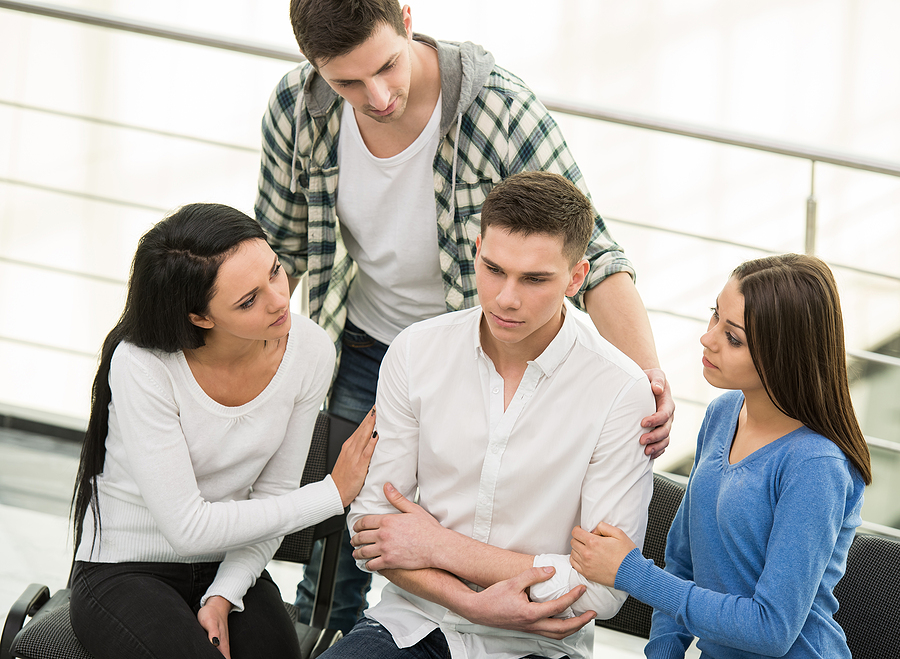
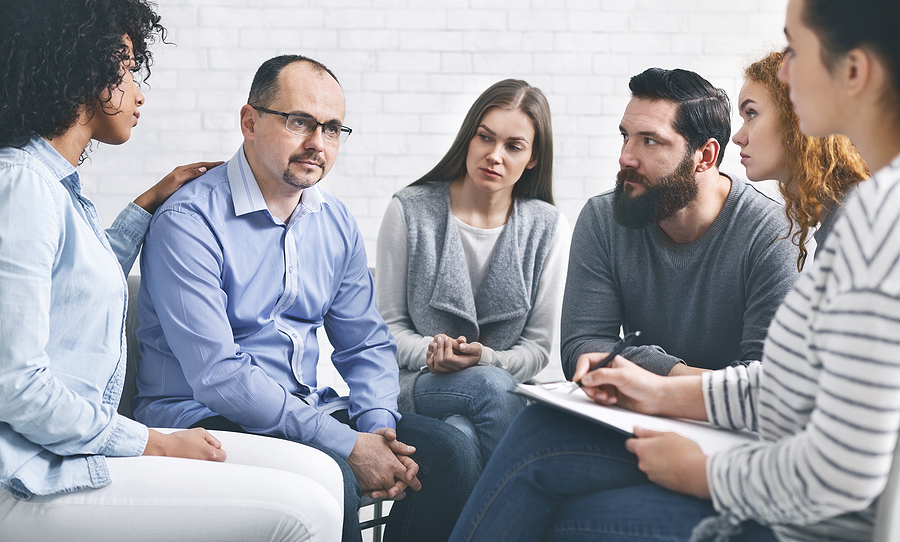
Each stage feeds into the next, and escaping feels impossible. Many people feel trapped in a cycle of hopelessness, believing no way out exists. Recognizing these stages helps both those struggling with addiction and their support systems. Effective interventions disrupt the cycle through therapy, support groups, and addiction treatment programs.
Why Breaking the Cycle Feels Difficult
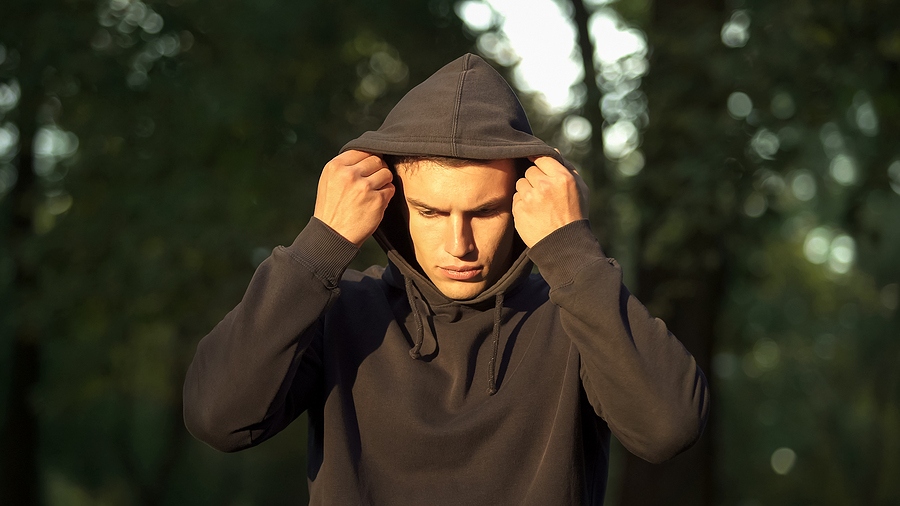
Substance use alters the brain’s reward system, creating intense cravings and withdrawal symptoms. This makes quitting feel impossible. Many return to substance use after attempting to quit. Emotional struggles also make recovery hard. Shame, guilt, and anxiety often prevent people from seeking help.
Fear of withdrawal and relapse discourages many from trying. The addiction cycle fosters a sense of defeat, making people feel powerless to change. Support from addiction treatment programs and mental health professionals provides a path forward. With resilience and encouragement, recovery remains possible.
Common Triggers That Fuel Addiction
Triggers often push people back into substance use. Environmental triggers include places linked to past drug or alcohol use. Emotional triggers involve stress, anxiety, or depression. Many turn to substances during difficult times, reinforcing addiction. Identifying triggers helps develop strategies to manage cravings and avoid relapse.
Social influences also contribute. Being around others who use substances normalizes the behavior. Peer pressure or the desire to escape reality pulls people back into addiction. A strong support system and healthy activities reduce the impact of these triggers. Avoiding high-risk situations plays a key role in staying sober.
How Physical and Mental Factors Contribute
Addiction affects both the body and mind. Substance use changes brain chemistry, creating dependence and cravings. Withdrawal symptoms range from discomfort to severe health risks, making it difficult to quit.
Mental health conditions such as depression, anxiety, and trauma often make addiction worse. Many use drugs or alcohol to cope with emotional pain, creating a destructive cycle. Addressing both physical and mental health improves recovery. Therapy and medical support help people regain control and end addiction.
Signs That Show the Cycle in Action
Behavioral and physical changes often signal addiction. Common signs include secrecy, withdrawal from social activities, and neglecting responsibilities. Physical symptoms include weight changes, poor hygiene, or health issues related to substance use.
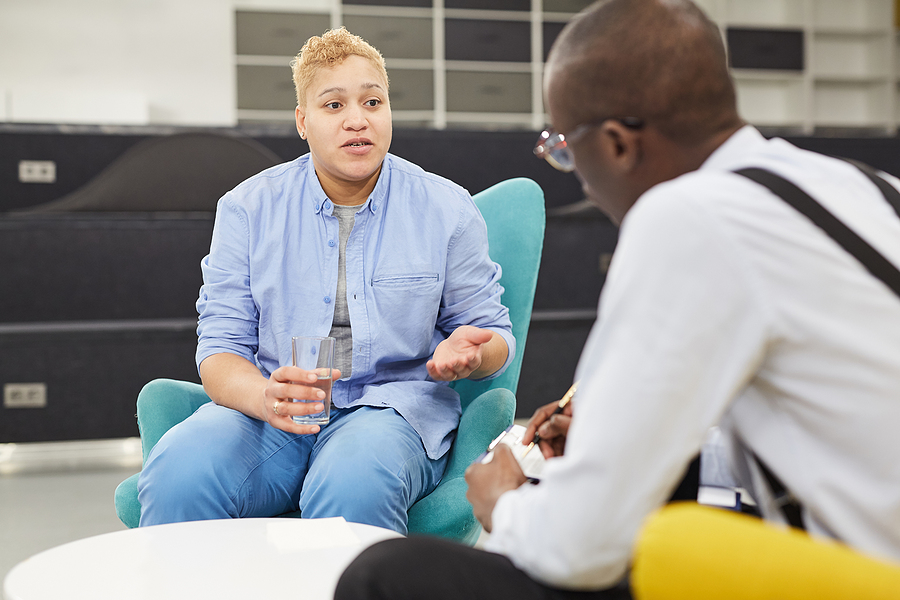
Emotional signs include irritability, anxiety, or mood swings. Many become defensive when questioned about their substance use, isolating themselves further. Recognizing these signs early increases the chance of successful intervention. Honest conversations help break through stigma and connect people with the treatment they need. Compassion and understanding make a difference for those struggling with addiction.
Steps to Break Free from Addiction
Recovery begins with acknowledging the problem and seeking support. Professional treatment, therapy, and support groups provide guidance. Removing triggers and making lifestyle changes helps maintain sobriety. A structured plan and strong support system improve the chances of long-term recovery.
Breaking free from addiction takes effort, but lasting change remains possible. Support exists for those ready to take the first step toward a healthier future. Contact Serenity Treatment Centers of Louisiana at (225) 361-8445 to discuss how to break the cycle of addiction with substance abuse treatment in Louisiana.